Written by Marijn Overvest | Reviewed by Sjoerd Goedhart | Fact Checked by Ruud Emonds | Our editorial policy
Procurement Department: How Does a Procurement Team Look and What are the Crucial Roles?
Key takeaways
- A procurement department is a branch in the company that takes care of the procurement business.
- The procurement department is headed by the director of procurement and where the procurement process starts and finishes.
- The procurement department’s important functions are sourcing, complying with policies, negotiation, contracting, and monitoring suppliers’ performance.
The procurement department is where it all happens. Every important procurement process starts in this very area where the procurement manager and his/her team discuss their strategies and options. As an upcoming or experienced procurement manager, your role is very important, which is why for today, we are going to discuss what the procurement department is all about.
We’ll cover the roles and the strategies that can be used. There are about 9 key roles that are very important in the procurement department, so we’ll cover those as well. After you are done reading this article, you should know those roles and possibly already have the right person in mind for these procurement roles.
In my experience as a procurement manager at Ahold, I have seen several companies that don’t have all of these different roles, some companies have even more roles and others name it differently.
However, it is important for every company to think about how they design their procurement department. I learned that procurement departments become more successful when these 9 roles are filled and collaborate well together.
Furthermore, I have created a free-to-download editable procurement process: 7 steps template. It’s a PowerPoint file, together with an Excel file, that can help you establish your procurement process in your department. I even created a video where I’ll explain how you can use this template.
Definition of Procurement Department
The procurement department of a company is responsible for buying and acquiring the goods the company sells. It interacts with suppliers and manufacturers to procure items and services that provide the best value for money.
Also called the purchasing or sourcing department, the physical procurement department is where the procurement process starts and finishes.
The procurement department is often headed by the director of procurement. They are the one who gathers the members of the procurement department.
The procurement director is also the one who assigns the tasks needed during the procurement process while checking to see if each process involved aligns with the strategies that the company wants for the procurement.
Finally, it is also in the procurement department where the final stages of the process are done. When the supplies are received in good condition, the suppliers paid, and contracts are negotiated, the procurement department takes care of all the necessary work to finalize the procurement process.
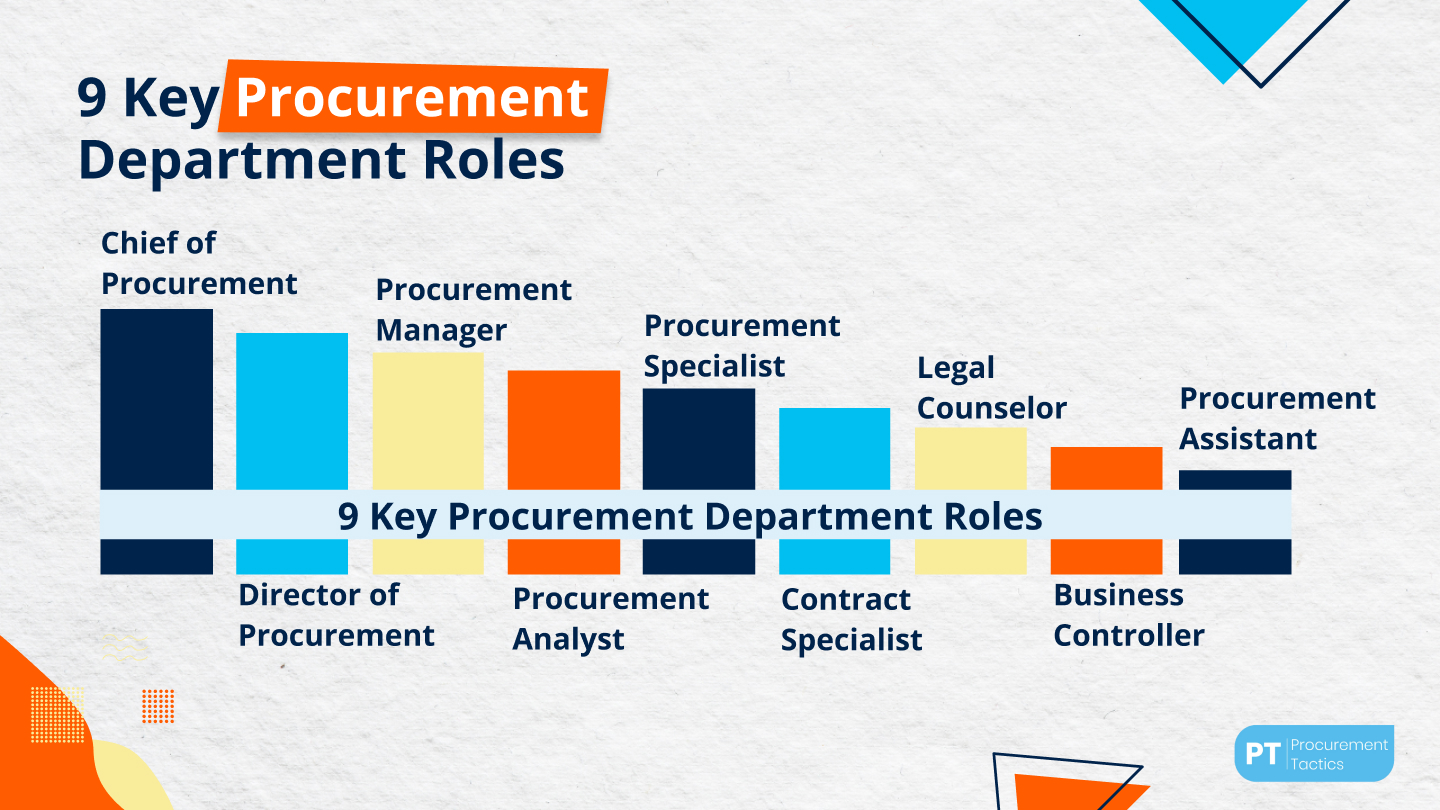
The 9 Key Procurement Department Roles
Since we’ve nailed down what the procurement department does and what it is made of, it’s time to check what its 8 key roles are.
Understand that each procurement role is dependent on one another. If the procurement department misses one, then it may present problems for the procurement process itself.
So without further ado, here are the 8 key procurement department roles:
1. Chief of Procurement
- Creating a long-term procurement strategy
- Leading a strong procurement team
- Manage Annual Organizational Budgets
- Develop an Organization’s purchasing policies
- Source, Negotiate, and Review Supplier Contracts
2. Director of Procurement
- Maintaining Knowledge of the market, citing current prices and fair rates for supplies.
- Monitoring, reviewing, and analyzing bids and quotes with potential suppliers.
- Monitoring, reviewing, and analyzing service agreements and contracts
- Overseeing sources for purchasing supplies
- Maintaining company budget and streamlining costs
3. Procurement Manager
- Manage Supplier Relations
- Identifying potential supplier sources
- Conducting interviews with potential vendors
- Negotiating good supplier agreements
- Managing supplier and vendor contracts
4. Procurement Analyst
- Meeting with vendors
- Testing products
- Negotiating supply contracts
- Creating cost reports
5. Procurement Specialist
- Supervise budget estimation and sourcing operations
- Maintain excellent communication with all business stakeholders
- Analyze offer and purchase bids and negotiate accordingly
- Assist in asset management procedures when required
6. Contract Specialist
- Manage contract development through all lifecycle stages
- Provide ongoing assistance to staff on contract development and compliance issues.
- Evaluate records for retention in compliance with Board-approved policies
7. Legal Counselor
- Provide Legal Guidance
- Conduct Legal Research
- Draft Legal Correspondence
- Ensure compliance with the law
8. Business Controller
- Analyzing and controlling the development of purchase prices
- Analyzing and controlling the impact from cost down projects and R&D projects
- Monthly reports and KPIs regarding procurement
- Forecasting the impact of procurement activities and development in purchase prices
- Prepare presentations for meetings
9. Procurement Assistant
- Assist Procurement Manager
- Set up conditions in the system
- Make sure that all prices (including price changes) are correct in the system
- Discuss administrative tasks with suppliers
What is a Procurement Team?
In project management, the term procurement refers to a group of professionals supervising the acquisition of needed goods and services as part of the project’s budget.
The procurement team is responsible for managing the procurement process and monitoring expenditures throughout the whole project lifecycle.
Additionally, they are tasked to negotiate with private or government contractors regarding the price, quality, and delivery terms. They then communicate with the project management team the necessary items and requirements of the project.
Important Functions of the Procurement Department
In the complex ecosystem of a modern organization, few departments hold as much influence over a company’s operational efficiency and financial health as the procurement department.
A well-functioning procurement department is not just about purchasing but about optimizing costs, ensuring quality, and fostering strategic relationships with suppliers.

1. Sourcing
Sourcing is the number one most important function of a procurement department. Why? Because the procurement department is responsible for purchasing goods or services that the company needs to operate.
It requires the procurement department to create a strategic plan to acquire the goods or services at the best possible price. Thus, it plays a huge part in the growth of the organization.
Of course, this starts by looking for potential suppliers. Selecting the best and most reliable supplier can have a huge impact on controlling costs.
2. Compliance with business policies
The procurement department must ensure that all its purchases are in compliance with the organization’s policies. Before purchasing,
It needs to look into the organization’s protocol to ensure that it complies with the budget approval. This will effectively help the organization to stay efficient with its costs.
3. Negotiation
The procurement department must have great negotiation skills to acquire the best materials at the lowest price.
This is vital to the profitability of the organization as high costs of materials can impact their revenue. If this happens, the growth of the organization will be slowed and will greatly affect its bottom line. Furthermore, if the procurement department would achieve a 1% price reduction, it will immediately impact the profitability of the company.
If you want to improve the negotiation skills (of your team), please take a look at our website for relevant courses.
4. Contracting
The procurement department offers the contract award to the best supplier. That is why the procurement department needs to scrutinize the supplier.
Furthermore, the procurement department must know and abide by all the agreements as it is vital to the success of the relationship between the organization and the supplier.
5. Monitors supplier’s performance
The procurement department’s important functions are sourcing, complying with policies, negotiation, contracting, and monitoring suppliers’ performance.
If it fails to monitor the supplier, it can be detrimental to the complete product and supply chain.
Componentsof Procurement
The following are the components of procurement:

1. People
This is the heart of procurement. They are the ones who are responsible for initiating and authorizing each step of the procurement process.
Without the people, nothing can be done in the procurement. There may be automation but there will be no one to maintain it without people in the procurement.
If you want to improve the procurement results then it is highly recommended to invest in your people. Make sure that the people have the right skills to be procurement professionals by giving them the right training.
Besides this, also think about where the mandate should be. It helps when procurement managers or their teams have the mandate to make the decisions. It will slow down the process when the mandate is centralized at the Chief of Procurement or the Director of Procurement.
2. Process
The process is the key to keeping the costs down and ensuring that the supplies are available when needed and that these are sourced for the best possible conditions. It helps improve and promote accuracy and timeliness in the procurement process.
3. Paperwork
Keeping records is important to make sure that every document is accessible when needed. Records act as a database of knowledge concerning payment terms and the supplier’s performance.
1st Procurement Expert’s Advice on Procurement Department
For this article, we asked a seasoned procurement professional to share his insights regarding procurement department.
Sjoerd Goedhart
Owner, Goedhart Interim Management & Consultancy
LinkedIn Profile: https://www.linkedin.com/in/sjoerdgoedhart/
1. What should readers know about the procurement department?
“Readers should be aware that the procurement department should be overseen by a Procurement Director/CPO, who must be a part of the company’s management team. This individual mustn’t report to a member of the management team such as Finance, Operations, or Sales.“
Follow-up Question: You mentioned that it doesn’t work for the procurement director/CPO to report to a member like Finance, Operations, or Sales. Can you explain why this reporting structure is less effective and how it may impact the effectiveness of the procurement function?
“The reporting structure where the procurement director reports to a department like Finance, Operations, or Sales is less effective because it hinders the independence of the procurement function. When procurement is part of another discipline, conflicts may arise, and decisions might be biased toward the host department’s priorities. This lack of balance can impede the procurement officer’s ability to advocate for essential considerations like risk management, sustainability, and compliance with regulations. For optimal functionality, the procurement department should operate independently within the company.“
2. What is the biggest misconception about the procurement department? What do most people get wrong about this topic?
“The role of a Procurement department is not just purchasing at the lowest cost. The department has a critical role in the entire company. A simple example; if the production department does not do its job properly, the company cannot produce. Sales cannot close profitable deals if there is no certainty and/or stability in the cost prices of products. These two examples show that the performance of a procurement department can have a huge impact on the performance of a company as a whole and on the profitability of the company.“
3. What are the critical functions of a modern procurement department in large organizations?
“The critical functions of a modern procurement department in large organizations include negotiating and purchasing, monitoring KPIs, ensuring compliance, and reporting on social and sustainable sourcing.“
4. How can procurement departments effectively collaborate with other departments to optimize organizational performance?
“By building relationships with key stakeholders, open communication channels, leveraging real-time data sharing, and involving departments in analytics-driven decision-making processes.
Integrating procurement with other business functions can improve efficiency, quality, innovation, and collaboration. By aligning procurement goals and strategies with the overall objectives and vision of the organization, you can reduce costs, waste, and risks, and increase value and performance.“
5. Are there any differences between the procurement and purchasing departments?
“Purchasing is short-term focused, while procurement has a long-term perspective. Short-term purchases should align with the overall long-term procurement strategy.“
6. What steps can procurement departments take to stay competitive in the modern procurement landscape?
“Procurement departments should embrace new technologies, particularly AI, to stay competitive in the modern landscape.“
2nd Procurement Expert’s Advice on Procurement Department
For this article, we asked another experienced procurement expert to share his insights to help answer common questions about the procurement department.
Elchin Musayev
Deputy Procurement Director, State Oil Company of the Republic of Azerbaijan (SOCAR)
LinkedIn Profile: linkedin.com/in/elchin-musayev
1. What do most people get wrong about the procurement department?
“One common misconception is that procurement is solely about cost reduction. In reality, it’s a strategic function that involves much more, including supplier relationships, sustainability, and aligning with the organization’s overall goals. It’s not a one-size-fits-all process and should be tailored to each organization’s unique needs.”
2. What should people know about the procurement department if they are planning to start working on this?
“People should know the following: Understand your organization’s goals and market trends. Be aware of procurement laws and regulations. Building good relationships with suppliers is key. Effective negotiation is crucial. Strong communication skills are vital. Be ready for changes in tech and regulations. Procurement is strategic, not just operational. Work closely with other departments. Be sensitive to global cultural differences. Consider ethical and sustainable practices.”
3. From your experience, what is the most important thing you learned about the procurement department?
“From my experience, I’ve learned that staying consistently updated with industry trends and regulations is paramount in procurement. Maintaining a systematic and organized approach helps navigate complex procurement processes effectively. Additionally, embracing challenges with readiness and an open mindset is crucial for growth in this field. Maintaining ethical and sincere conduct is not only a professional necessity but also a cornerstone of building trust in procurement relationships.”
4. What tips can you give them to be effective in their procurement department?
“1. Keep up with industry trends and regulations.
2. Foster strong connections with suppliers.
3. Develop effective negotiation techniques.
4. Maintain open and clear communication.
5. Be ready to adapt to changing tech and regulations.
6. Approach procurement as a strategic function.
7. Collaborate closely with other departments.
8. Understand and respect cultural differences.
9. Prioritize ethical and sustainable practices.”
5. Can you give us an example of how you led your purchasing department effectively?
“In my role as a procurement leader, I prioritize team dynamics and task delegation. We hold regular systematic team meetings and one-on-one catch-ups to ensure alignment and address individual needs. I’m focusing on the implementation of a robust follow-up and reporting system for accountability. Motivating my team to be proactive, open-minded, and share ideas is crucial. We’ve cultivated an open-door culture and a learning-by-example environment where I lead by setting an example.”
My Insight on Procurement Department
For this article I will also be sharing my insight about Procurement Department.
1. What is your experience within procurement departments and what can readers learn from this?
“I have worked in the procurement department of various companies like Ahold and Friesland Campina.
Through my experience, I learned that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to organizing procurement departments.
However, it is important to carefully consider the different roles and how they relate to each other.”
2. What should readers know about it?
“Procurement is a crucial department in any organization. It has a significant impact on a company’s key performance indicators such as revenue and margin, alongside sales.
To achieve the desired results, it is essential to organize the procurement department properly. Moreover, it is important to understand that procurement is more than just purchasing and should be approached strategically.
This involves determining the products the company wants to offer, selecting the right suppliers, and gathering the necessary data to make purchases more effectively.”
3. What is the biggest misconception about the procurement department? What do most people get wrong about this?
“One of the things I have to consider is that people have the idea that buyers are always tough negotiators. However, a good procurement manager knows that maintaining relationships is just as important as negotiating deals. Procurement remains people-oriented work, and therefore, it’s extremely important to continue working on the relational side as well.
In the past, I’ve been able to close fantastic deals because I really clicked with my contact person, and at the same time, I’ve also experienced situations where the relationship between two companies was strained because I didn’t get along well with the other company’s account manager.”
4. How can I improve the processes in the procurement department?
“I see three key ways to improve procurement. Firstly, it’s important that the significance of procurement is recognized and acknowledged throughout the entire company. The procurement management team plays a crucial role in this. They are responsible for setting the strategy and aligning it with the rest of the organization.
Secondly, to ensure success, it’s crucial to have a team with the right set of skills. All members should understand the concept of being tough on the issue but soft on the relationship. Additionally, they should receive good training and possess the right knowledge of procurement.
Lastly, it’s essential to place responsibilities in the right areas. Too often, I’ve seen the burden of responsibilities placed too high in the organization. This means that procurement managers and buyers aren’t empowered, and decisions aren’t made by those who work with them.”
5. How can the procurement department ensure quality when they are sourcing products? What are their usual KPIs when ensuring quality?
“Of course, a procurement department must ensure that they deliver quality. Some of the Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that fall under procurement are cost savings, the number of goods to be sold, and service level.”
Conclusion
The procurement department plays a crucial role in the success of an organization. It is not just limited to purchasing; instead, it encompasses strategic planning, negotiation, compliance, and relationship management.
The department requires a diverse skill set to perform its specified roles effectively. Monitoring supplier performance is also essential to maintain quality throughout the supply chain.
Therefore, organizations must prioritize the development and maintenance of a well-functioning procurement department. By doing so, they can ensure that they have a robust supply chain that supports their business goals, enhances their reputation, and drives their overall success.
Frequentlyasked questions
What is a procurement department?
A procurement department is a branch in any company that takes care of procurements.
How to construct a procurement department?
To construct a procurement department, you need a Director of Procurement, some procurement managers or directors, and procurement specialists.
What are key roles in a procurement department?
The key roles in a procurement department are sourcing, negotiations, competitor analysis, and supplier performance monitoring.
Want to Grow in Your Company’s Procurement Department?
Let’s face it; we all want to move up. Most especially if you’re working in your company’s procurement department.
We’ll show you how! Enroll in our Negotiation Course For Procurement Professionals and we’ll give you everything that you’ll need to bring up your negotiation game!
About the author
My name is Marijn Overvest, I’m the founder of Procurement Tactics. I have a deep passion for procurement, and I’ve upskilled over 200 procurement teams from all over the world. When I’m not working, I love running and cycling.


