Written by Marijn Overvest | Reviewed by Sjoerd Goedhart | Fact Checked by Ruud Emonds | Our editorial policy
Best 10 AI Tools in Warehouse Management
- AI in warehouse management uses machine learning, robotics, and real-time data to automate and optimize inventory and logistics operations.
- AI in warehouse management enhances efficiency by predicting demand, improving stock accuracy, and streamlining order fulfillment processes.
- AI-powered warehouse management leverages technologies like computer vision and predictive analytics to reduce errors and improve supply chain visibility.
AI in Warehouse Management Explained
AI in warehouse management refers to the use of artificial intelligence technologies (such as machine learning, computer vision, and robotics) to automate, optimize, and enhance warehouse operations. These systems analyze vast amounts of real-time and historical data to improve decision-making in areas like inventory tracking, space utilization, and order fulfillment. By leveraging AI, warehouses can predict demand more accurately, streamline picking and packing processes, and reduce operational errors and labor costs.
Modern AI-powered warehouse management systems optimize resource allocation, dynamically adjust storage strategies, and enhance visibility across the entire supply chain. As a result, companies achieve faster throughput, better scalability, and improved customer satisfaction, while reducing waste and increasing
Top 10 AI Tools in Warehouse Management
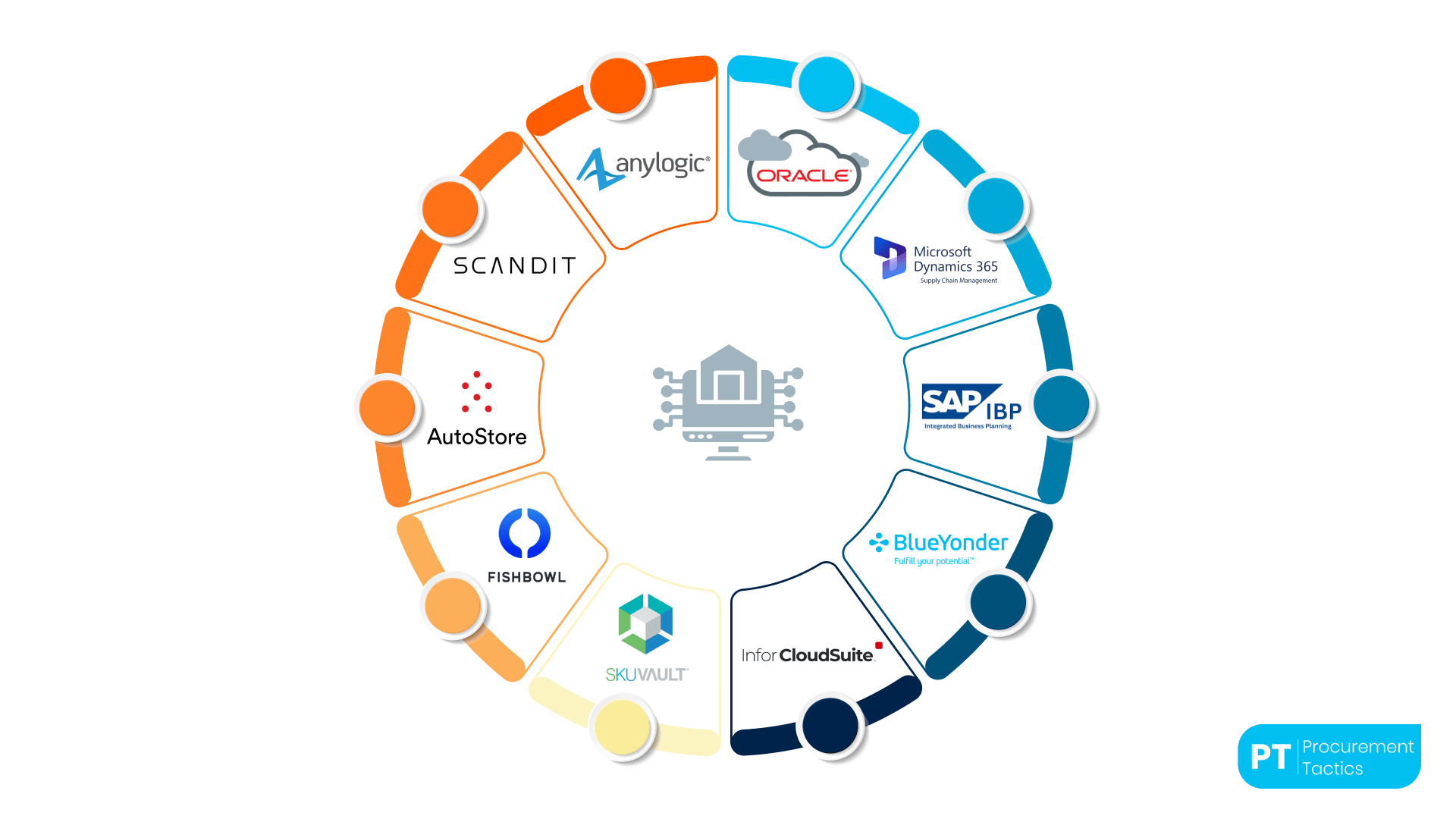
1. Oracle Inventory Management Cloud
Oracle offers an advanced AI-driven platform within its cloud ERP system that enables automated inventory management, warehouse space optimization, and improved demand forecasting.
The system uses machine learning to make real-time decisions, automate stock replenishment, and identify inefficiencies across the supply chain. It’s suitable for medium to large enterprises seeking full control over warehouse operations.
Price:
$50–$200 per user per month for SCM modules. Full ERP user access starts at $625/user/month.
2. Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management
Microsoft’s tool features an integrated AI assistant (Copilot) that helps managers respond quickly to supply chain disruptions, optimize product flows, and forecast delays. With integration into Power BI, users gain detailed data visualizations, and AI features support automation of ordering, workforce planning, and capacity adjustments.
Price:
Pricing not publicly available. Contact Microsoft for a tailored quote.
3. SAP Integrated Business Planning
SAP’s AI-powered system enables predictive planning, scenario simulations, and data integration from multiple sources to optimize inventory and warehouse workflows. By using digital twins and machine learning algorithms, the tool helps plan product flows, reduce stock levels, and improve delivery accuracy.
Price:
Not publicly disclosed, contact SAP for pricing.
4. Blue Yonder Luminate Logistics
Blue Yonder leverages AI and predictive models to enhance warehouse operations, such as automated sorting, dynamic inventory management, and workforce scheduling. The system analyzes goods movement and suggests optimal strategies in real time, making it ideal for retail, e-commerce, and 3PL operators.
Price:
Not publicly listed. Pricing available upon request.
5. Infor CloudSuite Inventory Management
Infor CloudSuite uses artificial intelligence to enhance inventory visibility across the entire supply chain. It automates reorder points, identifies inefficiencies within the warehouse, and supports faster decision-making. With a user-friendly interface and powerful analytics, it is adaptable to various industries.
Price:
Pricing not public, custom quote required.
6. SkuVault
SkuVault is a cloud-based warehouse management system that uses AI for inventory tracking, error detection, and goods flow optimization. It helps users reduce product loss, automate replenishment, and receive real-time alerts about process deviations. It’s especially useful for e-commerce businesses and sellers with multiple warehouses.
Price:
Starts at $269.08/month; PRO at $404.08, and ENTERPRISE at $809.08/month.
7. Fishbowl Inventory
Fishbowl combines classic ERP functionality with AI-powered data analysis. It automates order processing, tracks serial and lot numbers, and forecasts inventory needs. The tool is great for manufacturers and distributors looking for higher precision and fewer manual errors in warehouse handling.
Price:
Not publicly disclosed. Contact the provider for pricing.
8. AutoStore (CarouselAI)
AutoStore is a robotic storage and retrieval system that uses AI to optimize warehouse space and automate picking operations. Its CarouselAI technology enables robots to navigate a grid of bins and deliver required items efficiently, offering high-density storage and faster order processing.
Price:
Not public; pricing provided on request from AutoStore.

9. Scandit Smart Data Capture
Scandit leverages AI-powered computer vision technology to enable fast and accurate barcode scanning on mobile devices. With features like multi-code scanning and augmented reality (AR), it helps warehouse workers quickly locate and verify products, increasing accuracy and efficiency.
Price:
Not listed publicly. Enterprise pricing is available via inquiry.
10. AnyLogic
AnyLogic and its logistics module, AnyLogistix, allow users to simulate and model warehouse operations through digital twins. Supported by AI algorithms, users can analyze scenarios like increased order volumes, robot integration, or layout changes before implementing them in the real world.
Price:
Not publicly available. Pricing offered upon contact.
AI Technologies in the Warehouse
1. Machine Learning (ML)
ML enables warehouse systems to analyze historical and real-time data to make accurate predictions and optimize operations. ML algorithms can forecast demand, optimize stock levels, and reduce overstock or stockouts. By learning from past order patterns and operational behavior, ML enhances everything from inventory planning to labor forecasting.
2. Computer Vision
Computer vision allows machines to interpret and process visual information from cameras and sensors in the warehouse. This technology is used for object recognition, barcode scanning, and monitoring shelf levels. It helps automate quality control, identify misplaced inventory, and ensure accurate product handling without human intervention.
3. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
AMRs are intelligent robots equipped with AI that navigate warehouse floors independently. Unlike traditional AGVs, AMRs use sensors and onboard computing to adapt to dynamic environments, avoid obstacles, and optimize travel paths. They are commonly used for picking, transporting, and sorting goods, significantly reducing manual labor.
4. Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics combines AI and data modeling to anticipate future warehouse needs. It enables managers to proactively address potential disruptions, schedule maintenance, and align resources with expected demand. This forward-looking approach enhances efficiency, minimizes downtime, and supports smarter decision-making.
5. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP enables voice-directed warehouse systems and chatbots to understand and respond to human language. This technology supports hands-free operations, allowing workers to receive instructions or input data using simple voice commands. It reduces training time and improves task accuracy and safety.
6. Digital Twins
Digital twins create virtual models of warehouse operations that mirror real-world conditions. AI uses these simulations to test various scenarios, such as layout changes or order surges, before implementing them physically. This helps optimize workflows, evaluate risks, and reduce planning errors.
7. Edge AI
Edge AI processes data directly on local devices (such as cameras or robots) instead of sending it to the cloud. In warehouse settings, this means faster decision-making, lower latency, and increased operational speed. It supports real-time safety alerts, faster item recognition, and immediate quality control actions.
Benefits of AI in the Warehouse
Implementation Challenges of AI in Warehouse
AI Impacts in Warehouse Management
AI has significantly transformed warehouse management by introducing automation, real-time data processing, and intelligent decision-making. From streamlining inventory control to optimizing pick-and-pack operations, AI technologies help reduce errors, increase productivity, and ensure faster order fulfillment. Warehouses now operate with greater agility, adapting quickly to changes in demand while maintaining high levels of accuracy and customer satisfaction.
Beyond operational improvements, AI also impacts strategic planning and long-term warehouse performance. With predictive analytics and digital twins, managers can simulate scenarios, forecast trends, and make proactive decisions. Additionally, AI enhances workforce safety by taking over repetitive or hazardous tasks and supports sustainable practices by reducing waste and energy consumption, making warehouse operations smarter and more responsible.
Conclusion
AI in warehouse management is revolutionizing how modern logistics operate by combining technologies like machine learning, computer vision, and robotics to automate and enhance every aspect of warehouse workflows.
From predictive inventory control and autonomous robots to real-time data analytics and digital twins, AI tools improve efficiency, accuracy, and scalability while reducing operational costs and manual labor.
Although the implementation comes with challenges such as high initial investment and system integration, the long-term benefits, such as faster order fulfillment, better decision-making, and improved sustainability, position AI as a critical driver of the future-ready warehouse.
Frequentlyasked questions
What is AI in warehouse management?
AI in warehouse management uses machine learning, robotics, and real-time data to automate and optimize inventory and logistics operations.
What are the main challenges of implementing AI in warehouse management?
The main challenges of implementing AI in warehouse management include high initial investment, system integration issues, and the need for clean data and technical expertise.
What AI technologies are used in warehouse management?
Warehouse management uses AI technologies such as machine learning, computer vision, autonomous mobile robots, and predictive analytics to automate operations and improve efficiency.
About the author
My name is Marijn Overvest, I’m the founder of Procurement Tactics. I have a deep passion for procurement, and I’ve upskilled over 200 procurement teams from all over the world. When I’m not working, I love running and cycling.






